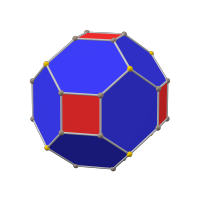
Chamfered cube
| Chamfered cube | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Rank | 3 |
| Type | Near-miss |
| Notation | |
| Conway notation | cC |
| Elements | |
| Faces | 6 squares, 12 rectangular-symmetric hexagons |
| Edges | 24+24 |
| Vertices | 8+24 |
| Vertex figures | 8 equilateral triangles |
| 24 isosceles triangles | |
| Measures (edge length 1) | |
| Dihedral angles | 4-6: 135° |
| 6-6: 120° | |
| Central density | 1 |
| Number of external pieces | 18 |
| Level of complexity | 4 |
| Related polytopes | |
| Army | Chamfered cube |
| Regiment | Chamfered cube |
| Dual | Tetrakis cuboctahedron |
| Conjugate | None |
| Abstract & topological properties | |
| Flag count | 192 |
| Euler characteristic | 2 |
| Surface | Sphere |
| Orientable | Yes |
| Genus | 0 |
| Properties | |
| Symmetry | B3, order 48 |
| Flag orbits | 4 |
| Convex | Yes |
| Nature | Tame |
The chamfered cube, also known as the order-4 truncated rhombic dodecahedron, is one of the near-miss Johnson solids. It has 6 squares and 12 hexagons as faces, and 32 order-3 vertices divided into two sets of 8 and 24 each. It can be made equilateral, but the hexagons have two angle sizes.
Assuming they are equilateral, the hexagonal faces have angles of on one pair of opposite vertices, and angles of on the four remaining vertices.
The canonical variant with midradius 1 has two edge lengths: one of length and the other of length with the same dihedral angles as the equilateral variant.
It can also be viewed as an order-4-truncated rhombic dodecahedron, or as an octahedrally-symmetric Goldberg polyhedron of index (2,0).
It is the convex core of the uniform quasirhombicuboctahedron and of the compound rhombihexahedron.
Vertex coordinates[edit | edit source]
The vertices of an equilateral chamfered cube can be given by all changes of sign of:
- ,
along with all permutations and changes of sign of:
- .
External links[edit | edit source]
- Klitzing, Richard. "Chamfered cube".
- Wikipedia contributors. "Chamfered cube".
- McCooey, David. "Chamfered Cube (all edges equal)"





