Faceted hexacosichoron
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Faceted hexacosichoron | |
|---|---|
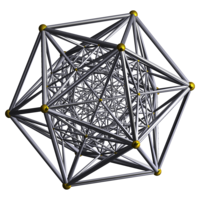 | |
| Rank | 4 |
| Type | Regular |
| Notation | |
| Bowers style acronym | Fix |
| Coxeter diagram | o5/2o5o3x ( |
| Schläfli symbol | |
| Elements | |
| Cells | 120 icosahedra |
| Faces | 1200 triangles |
| Edges | 720 |
| Vertices | 120 |
| Vertex figure | Great dodecahedron, edge length 1 |
| Edge figure | ike 3 ike 3 ike 3 ike 3 ike 3 |
| Deep holes | Triangles |
| Measures (edge length 1) | |
| Circumradius | |
| Edge radius | |
| Face radius | |
| Inradius | |
| Hypervolume | |
| Dichoral angle | 120° |
| Central density | 4 |
| Number of external pieces | 2400 |
| Level of complexity | 4 |
| Related polytopes | |
| Army | Ex |
| Regiment | Ex |
| Company | Ex |
| Dual | Small stellated hecatonicosachoron |
| Conjugate | Great faceted hexacosichoron |
| Convex core | Hecatonicosachoron |
| Abstract & topological properties | |
| Flag count | 14400 |
| Euler characteristic | 480 |
| Schläfli type | {3,5,5} |
| Orientable | Yes |
| Properties | |
| Symmetry | H4, order 14400 |
| Convex | No |
| Nature | Tame |
The faceted hexacosichoron, or fix, also commonly called the icosahedral 120-cell, is one of the 10 Schläfli–Hess polychora. It has 120 icosahedra as cells, joining 5 to an edge and 12 to a vertex in the form of a great dodecahedron.
As the name suggests, it is a faceting of the hexacosichoron, sharing its vertices, edges, and faces. The icosahedral cells are the same as the vertex figures of the hexacosichoron.
Cross-sections[edit | edit source]
Vertex coordinates[edit | edit source]
Its vertices are the same as those of its regiment colonel, the hexacosichoron.
Related polychora[edit | edit source]
Uniform polychoron compounds composed of faceted hexacosichora include:
- Faceted chirotetrahedral dishexacosichoron (2)
- Faceted snub pentishecatonicosachoron (5)
- Chiricosahedral hyperprismatochoron (6)
- Faceted snub decahecatonicosachoron (10)
- Disicosahedral hyperprismatochoron (12)
External links[edit | edit source]
- Bowers, Jonathan. "Category 1: Regular Polychora" (#7).
- Klitzing, Richard. "fix".
- Nan Ma. "Icosahedral 120-cell {3, 5, 5/2}".
- Wikipedia contributors. "Icosahedral 120-cell".















