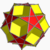
Small stellated dodecahedron
| Small stellated dodecahedron | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Rank | 3 |
| Type | Regular |
| Notation | |
| Bowers style acronym | Sissid |
| Coxeter diagram | x5/2o5o ( |
| Schläfli symbol |
|
| Elements | |
| Faces | 12 pentagrams |
| Edges | 30 |
| Vertices | 12 |
| Vertex figure | Pentagon, edge length (√5–1)/2  |
| Petrie polygons | 10 skew hexagons |
| Holes | 20 triangles |
| Measures (edge length 1) | |
| Circumradius | |
| Edge radius | |
| Inradius | |
| Volume | |
| Dihedral angle | |
| Central density | 3 |
| Number of external pieces | 60 |
| Level of complexity | 3 |
| Related polytopes | |
| Army | Ike, edge length |
| Regiment | Sissid |
| Dual | Great dodecahedron |
| Petrie dual | Petrial small stellated dodecahedron |
| φ 2 | Great icosahedron |
| κ ? | Petrial icosahedron |
| Conjugate | Great dodecahedron |
| Convex core | Dodecahedron |
| Abstract & topological properties | |
| Flag count | 120 |
| Euler characteristic | -6 |
| Schläfli type | {5,5} |
| Surface | Bring's surface[2] |
| Orientable | Yes |
| Genus | 4 |
| Skeleton | Icosahedral graph |
| Properties | |
| Symmetry | H3, order 120 |
| Flag orbits | 1 |
| Convex | No |
| Nature | Tame |
| History | |
| Discovered by | Johannes Kepler[note 1] |
| First discovered | 1613 |
The small stellated dodecahedron, or sissid, is one of the four Kepler-Poinsot solids. It has 12 pentagrams as faces, joining 5 to a vertex.
It is the first stellation of a dodecahedron, from which its name is derived.
Small stellated dodecahedra appear as cells in two nonconvex regular polychora, namely the small stellated hecatonicosachoron and grand stellated hecatonicosachoron.
Vertex coordinates[edit | edit source]
The vertices of a small stellated dodecahedron of edge length 1, centered at the origin, are all cyclic permutations of
- .
Related polytopes[edit | edit source]
Alternative realizations[edit | edit source]
The small stellated dodecahedron and the great dodecahedron are conjugates. Thus they are both faithful symmetric realizations of the same abstract regular polytope, {5,5∣3}. This abstract polytope is a quotient of the order-5 pentagonal tiling which tessellates Bring's surface. There are in total 6 faithful symmetric realizations of the underlying abstract polytope. The great dodecahedron and the small stellated dodecahedron are the only pure faithfully symmetric realizations, the others are the results of blending those two along with {5,5∣3}/2.
| Dimension | Components | Name |
|---|---|---|
| 3 | Great dodecahedron | Great dodecahedron |
| 3 | Small stellated dodecahedron | Small stellated dodecahedron |
| 6 | ||
| 8 | ||
| 8 | ||
| 11 |
Compounds[edit | edit source]
Two uniform polyhedron compounds are composed of small stellated dodecahedra:
In vertex figures[edit | edit source]
The small stellated dodecahedron appears as a vertex figure of two Schläfli–Hess polychora.
| Name | Picture | Schläfli symbol | Edge length |
|---|---|---|---|
| Great faceted hexacosichoron |  |
{3,5/2,5} | |
| Great hecatonicosachoron |  |
{5,5/2,5} |
External links[edit | edit source]
- Bowers, Jonathan. "Polyhedron Category 1: Regulars" (#7).
- Bowers, Jonathan. "Batch 2: Ike and Sissid Facetings" (#1 under sissid).
- Klitzing, Richard. "Sissid".
- Nan Ma. "Small stellated dodecahedron {5/2, 5}".
- Wikipedia contributors. "Small stellated dodecahedron".
- McCooey, David. "Small Stellated Dodecahedron"
- Hartley, Michael. "{5,5}*120".
- Wedd, N. S4:{5,5}
Notes[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Earlier authors drew shapes the Small stellated dodecahedron or similar shapes earlier, however Kepler was the first to recognize the Small stellated dodecahedron as regular, and explicitly describe it.
References[edit | edit source]
Bibliography[edit | edit source]
- McMullen, Peter; Schulte, Egon (1997). "Regular Polytopes in Ordinary Space" (PDF). Discrete Computational Geometry (47): 449–478. doi:10.1007/PL00009304.
- Weber, Matthias (2005). "Kepler's small stellated dodecahedron as a Riemann surface" (PDF). Pacific Journal of Mathematics. 220 (1): 167–182. doi:10.2140/pjm.2005.220.167.